[ad_1]
What GAO Found
In November 2022, the Department of Defense (DOD) completed its multiyear transition of military medical treatment facilities from the military departments—the Army, the Navy, and the Air Force—to the Defense Health Agency (DHA). This means DHA is responsible for the management and administration of about 700 facilities (including dental clinics) in the United States and overseas. DOD accomplished the transition with a series of steps following a 2019 plan. For example, DHA grouped facilities into 36 markets in the United States and two regions overseas and established 22 offices to manage them. DHA relies on the military departments to provide active-duty personnel to staff the facilities and the offices, and augments them with civilian employees and contractors.
DHA is working to mitigate staffing shortfalls at the military medical treatment facilities that predated the transition. For example, DHA and the military departments agreed on a process to staff military personnel to all facilities in 2024 and beyond. However, DOD has not studied and validated the number of personnel required to staff the market and regional offices. The estimate of over 1,400 personnel for the 22 offices could be higher than needed and exceeds expected budgetary and personnel resources. DHA has faced difficulties staffing these offices with military and civilian personnel in the first years of operations. Yet, DOD has not revaluated the efficiency of the current structure since adopting it in 2019 to replace the 2018 plan. The 2018 plan would have established two U.S. regions with two offices each, compared with the 2019 plan’s 20 offices to manage 36 markets (see fig.). Until DOD reevaluates the efficiency of the market structure and updates personnel requirements, DOD may risk not accomplishing its vision for an integrated health delivery system that efficiently uses available personnel and budgetary resources.
Changes to DHA’s Management Structure for Military Medical Treatment Facilities
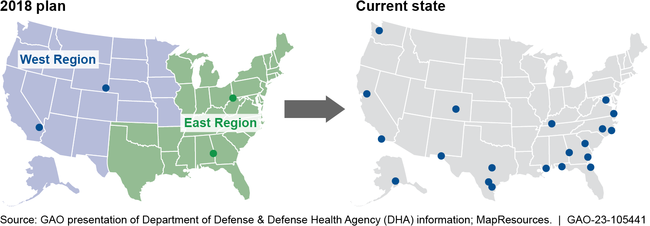
Note: The two DHA overseas regions did not change after 2018 and so are not shown here.
DOD officials stated that the transition may lead to savings in future years as DHA matures its managerial capabilities, but GAO found that the extent to which DOD has realized or will realize savings is unclear. For example, in fiscal year 2022, DHA began 10 initiatives reforming clinical and business processes to save over $1.6 billion by fiscal year 2026. However, DOD officials were unable to identify performance goals to track execution of the initiatives. Without doing so, DOD may not know whether the initiatives are achieving intended cost savings.
Why GAO Did This Study
The National Defense Authorization Act for Fiscal Year 2017 mandated sweeping reforms to the military health system, including transitioning military medical treatment facilities to DHA. These facilities deliver health care to service members to ensure their medical readiness. The facilities also provide essential on-the-job training for active-duty medical providers, and care for service members’ families, retirees, and other eligible beneficiaries.
The joint explanatory statement accompanying the Consolidated Appropriations Act for Fiscal Year 2021 includes a provision for GAO to review the transition. This report examines (1) the status of the transition of facilities to DHA management, and the extent to which DHA has (2) addressed any transition-related staffing challenges and (3) identified cost savings and assessed efficiency initiatives.
GAO reviewed DOD reports and briefings and analyzed data on medical headquarters personnel numbers and budgetary resources, both before and after the transition. GAO interviewed DOD officials from six market offices and six facilities selected on the basis of market establishment date, patients served, and location.
[ad_2]
Source link
