[ad_1]

Introduction
Small Business Lending Statistics: Small company loans are an integral component of our economy, fuelling development, innovation, and job creation. Statistics on small company loans provide insight into entrepreneurship health and capital availability; recent figures reveal that approximately 50 % of commercial loans made recently went towards small enterprises; however, access to funds still poses difficulties for some small enterprises owned by women, minorities, or underprivileged groups.
Studies show that these groups often encounter greater obstacles and lower loan acceptance rates than their peers. With the rise of online lenders and alternative financing solutions, technological improvements have also had an effect on lending markets; such approaches make money acquisition easier and faster – this makes analyzing current small business loan statistics essential for policymakers, lenders, and entrepreneurs alike as small firms remain crucial components of economic growth.
Editor’s Choice
- Launching a small firm can often be completed within four days in the US.
- Due to insufficient funding, 38% of small firms close.
- Most small company owners make less than $70,000 each year from their businesses.
- Over 100,000 Black-owned enterprises operate within the US.
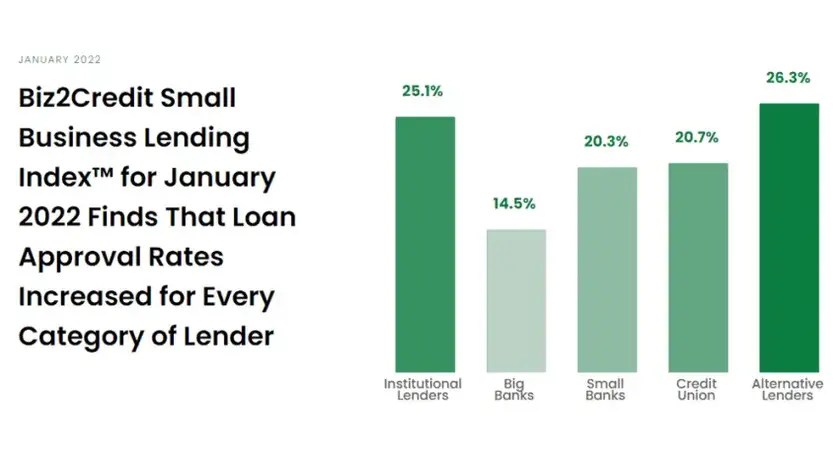
- Alternative lenders currently boast an acceptance rate of 24.5% on loans issued through alternative lending channels.
- Less than 15% of loan requests from small businesses are approved by large banks.
- 32% of small business owners used internet loans.
- Small enterprises typically borrow approximately $107,000 on average for financing needs.
- Less than 40% of newly founded small companies are led by women of color.
- Women of color running companies saw their numbers increase by 43% over 2015.
- Black-owned companies were able to generate total sales of approximately $206 billion.
- Up to half of US commerce is conducted by small businesses.
(Source: Smallbiztrends.com)
What is Small Business Lending?
Small business financing refers to providing funds to small businesses for various purposes, such as starting or expanding operations, purchasing inventory or equipment, meeting labor shortages, or fulfilling other working capital requirements. Promoting entrepreneurship, driving economic expansion, and creating employment prospects requires financing from multiple institutions, including conventional banks, credit unions, Community Development Financial Institutions (CDFIs), and internet lenders. Many financial organizations offer assistance to small company borrowers. Lenders typically assess a small firm’s creditworthiness using various criteria, including financial statements, credit histories, business plans, and collateral. Interest rates, grace periods, and loan amounts will depend on which lender meets specific firm needs.
For company owners to invest in their businesses, pursue growth prospects, and overcome financial hurdles, small business loans are necessary. Small enterprises often face difficulty accessing capital due to their small asset bases, lack of credit histories, and increased operational risks. There may also be additional barriers to getting small company loans for certain groups, including women-owned firms and minority-run enterprises in underdeveloped areas. Recent technological developments have dramatically transformed the small company loan market. Online lenders and alternative finance platforms now provide more convenient application processes, faster funding times, and flexible loan requirements than ever. As an easy alternative to conventional loan sources, these platforms evaluate borrowers’ creditworthiness with algorithms and data analytics. While these choices make funding more readily accessible for some business owners, they could come with higher interest rates or costs associated with them.
Small company financing is vitally important and governments and politicians frequently implement programs designed to facilitate access. Measures intended to improve small company owners’ financial literacy and management abilities may include loan guarantee schemes, tax incentives, or capacity-building activities. Small company financing also has significant economic benefits as it promotes entrepreneurship, fosters innovation, and generates job opportunities; to support economic growth and maintain a vibrant entrepreneurial ecosystem it’s crucial that there be equal access to finance for all small enterprises and an environment that makes securing financing simpler for them.
Types of Small Business Loan
Entrepreneurs and company owners can apply for several small business loans depending on the firm’s requirements, finances, and borrowing goals. A specific loan type may apply.
- Term loans are one of the simplest and most accessible forms of small company financing, lending you money over time with regular installments. They can be used to fund inventories, expand operations, or purchase equipment.
- Small Business Administration (SBA) loans are issued by qualified lenders but backed by the U.S. Small Business Administration. Through various lending programs offered by SBA – like 7(a), which offers loans for general purposes, and CDC/504 designed specifically to help acquire assets such as real estate and equipment – small business owners have access to SBA loans at very competitive rates.
- Equipment loans are loans designed specifically to finance the acquisition of machinery or other equipment for businesses. Sometimes the equipment being funded can even serve as collateral against its loan approval process.
- Business lines of credit provide flexible financing with predetermined credit limits that allow businesses to borrow as needed with only interest charged on what was borrowed. They’re an effective solution for controlling cash flow fluctuations, meeting immediate expenses, or capitalizing on opportunities.
- Accounts receivable finance (or invoice financing) refers to borrowing against past-due bills from clients. Lenders collect payment directly from consumers and advance a portion of the invoice amount as advance. It can be particularly helpful for businesses that require longer payment cycles or need quick cash flows quickly.
- Technically speaking, merchant cash advances aren’t loans but rather advances on future credit card purchases. Lenders make a one-time lump sum payment and then collect repayment by taking a portion of each day’s sales of credit cards. Businesses with strong sales may find this solution advantageous but the costs may increase significantly.
- Microloans, typically offered by nonprofit institutions or local lenders, are designed to aid extremely small firms or new ventures. Compared with traditional loans, they usually feature lower credit amounts and more flexible restrictions.
General Small Business Loan
Small business loan data provide insight into the state of access to capital for small firms, their borrowing patterns, and the overall lending environment.
- Small businesses often face difficulty when trying to acquire financing. According to the Biz2Credit Small Company Lending Index; banks have historically accepted about 13-15% of small company loan applications from commercial banks; acceptance rates among alternative lenders are slightly higher – reaching around 56%.
- Small firms may receive loans of various amounts depending on their requirements and financial situations; with 7(a) loans issued through the SBA being the most popular credit program reported to average approximately $536,000 during the fiscal year 2022, according to their estimates.
- Small business loans are used for many different reasons. According to a poll conducted by the Federal Reserve Banks, three of the top reasons companies sought financing were: maintaining working capital requirements; expanding operations; and purchasing inventory or equipment.
- Major national banks typically lend loans of $593,000 in most instances.
- Alternative lenders typically provide small business loans between $50K to $80K from these sources.
- Different lenders, such as traditional banks, credit unions, internet lenders, and alternative finance platforms provide loans to small companies. According to the Federal Reserve Small Business Credit Survey in 2022, 61% of loan applications accepted were by small banks versus 38% accepted by large banks.
- Demographic groupings may experience differing degrees of access to small company financing, with women and minorities often experiencing difficulty getting loans. Black-owned firms had the highest denial rates in 2022 according to data from Federal Reserve Banks; Hispanic businesses and women-owned firms followed behind.
- Due to the rise of online lending platforms, the lending environment for small companies has significantly altered. According to estimates by the Small Business Credit Survey, 32% of small employer businesses requested loans online in 2022; unlike traditional lenders, these platforms offer faster loan processing periods, easier application procedures, and greater accessibility than their predecessors.
- COVID-19 had a devastating impact on small business lending. To alleviate its consequences, the Paycheck Protection Program (PPP) offered forgiven debts for small companies affected by COVID. According to the SBA, approximately $800 billion worth of PPP loans had been authorized as of 2022 – providing relief for millions of enterprises worldwide.
(Reference: zippia.com)
Small Business Financial Statistics
Small business financial data provides insight into the state, effectiveness, and challenges of their finances.
- Income for small businesses varies significantly across industries and types, with average yearly revenues estimated by the Small Business Administration ranging from less than $50,000 for micro businesses to over $5 million for larger ones in the U.S. However, income can change greatly depending on factors like location, sector of operation, or stage in the company’s lifecycle.
- Profitability is key for small businesses’ financial well-being, with around half of US firms expected to be profitable in 2022 according to JP Morgan Chase analysis. Pricing tactics, operational effectiveness, and other variables all play a part in profitability.
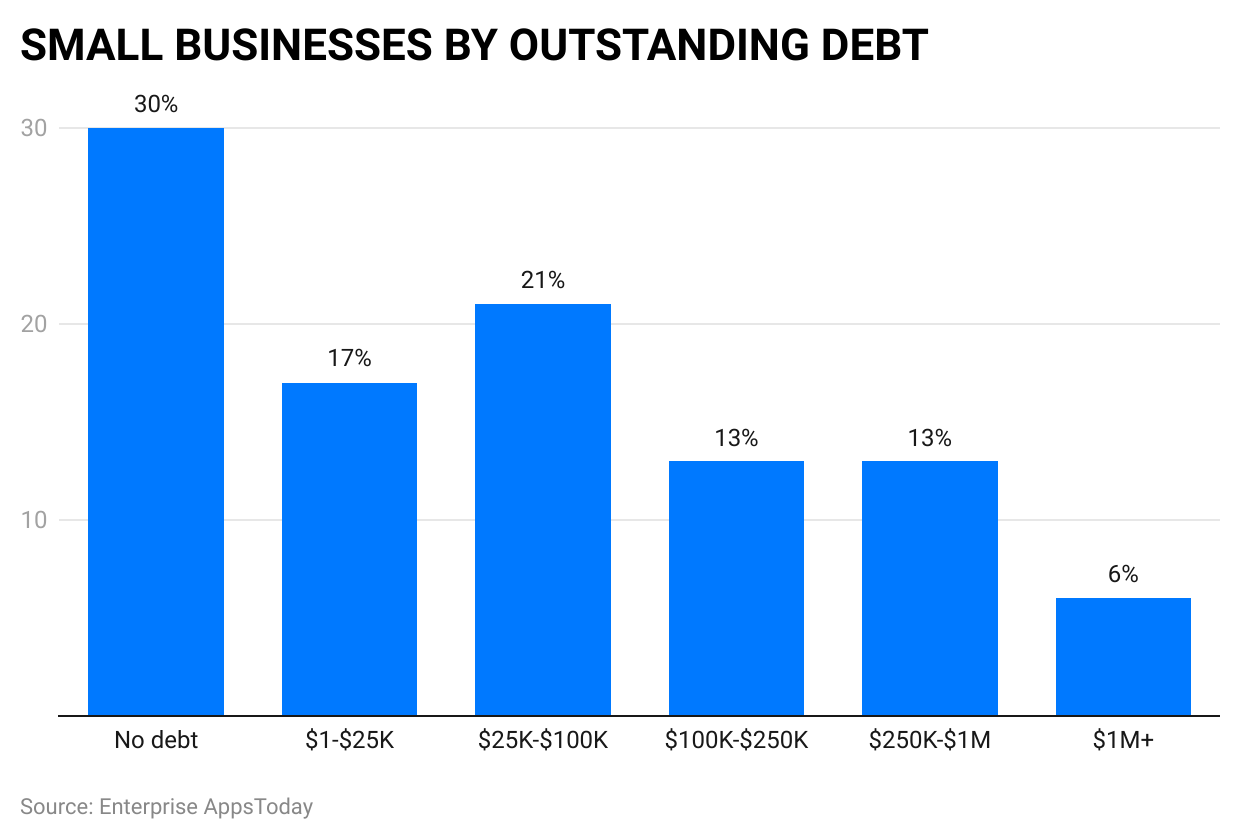
- At least 70% of small firms in the United States; have outstanding debt.
- Small Business Administration (SBA) loans typically total $417,316.
- An interest rate on a small business loan typically ranges between 2.54% and 7.01%.
- Only 33% of small enterprises survive for 10 years.
- Cash flow is a fundamental element of small business financing, representing the flow of money in and out of a company. According to U.S. Bank research, cash flow issues were identified as one of the primary reasons for small business failure. For ongoing operations it’s critical that cash flows are effectively managed; keeping an eye on payables and receivables and anticipating cash requirements in order to predict cash requirements accurately.
- Debt finance is often utilized by small firms for expansion and daily operations. According to the Small Business Association (SBA), on average a typical small firm had about $195,000 in outstanding debt in the 2022 fiscal year alone. Financial stability depends on keeping debt levels under control while making sure debt payments can be met without difficulty.
- Profit margins measure the portion of income that remains profitable after expenses have been subtracted, and industry differences in small firm profit margins can be dramatic. According to Sageworks’ financial information provider statistics, in recent years the average net profit margin across all industries for small firms was approximately 7%; however, certain sectors such as professional services or technology may experience larger profit margins.
- Small firms face numerous financial hurdles. According to the Federal Reserve’s Small Business Credit Survey, these include managing operating expenditures, accessing credit, and gaining new clients – the primary issues confronted by small firms. Other potential obstacles can include a lack of cash, excessive costs, or unpredictable economic conditions.
- Small companies rely on various funding sources. According to the Federal Reserve’s Small Company Credit Survey in 2022, bank loans, company credit cards, and personal cash were among the three most frequently utilized by small firms as sources of funding; however; alternative sources like crowdsourcing and internet lenders have become increasingly popular options in recent years.
US Small Business Loan Statistics
Information on financing environments and small enterprises may be gained through statistics regarding small business loans in the US.
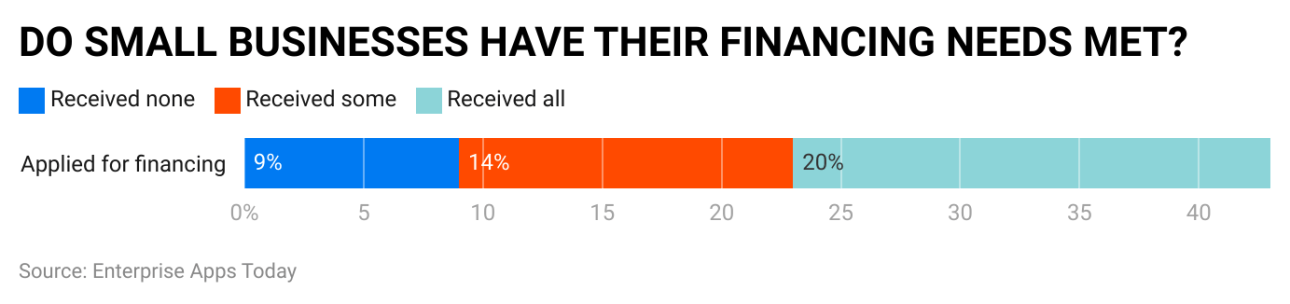
- According to the Federal Reserve’s Small Company Credit Survey, around 60% of loan applicants for small companies were approved in 2022 at least partially for some of the capital they requested; this rate may differ depending on a variety of factors including borrower creditworthiness, the financial performance of the company, type of lender and more.
- The size of a Small Business Loan Depends on the firm type, sector, and financing needs. One loan program offered by the Small Business Administration (SBA) had an average loan amount of $536,000 in the fiscal year 2022; conventional banks and loans ranging from a few thousand dollars to several million dollars are offered on online markets.
- Small firms apply for loans for various reasons, as per the Federal Reserve’s Small Company Credit Survey. According to this data, in 2022 the most prevalent reasons will include meeting working capital requirements (46%), funding company development or investment possibilities (41%), and buying inventory or equipment (36%).
- Different lenders provide loans to small enterprises. Finance may come from conventional banks, credit unions, online lenders, or alternative finance platforms. According to the Federal Reserve in 2022, large banks approved approximately 38% of loan requests from small businesses while smaller banks approved approximately 61%.
- Small company loans were dramatically altered by the COVID-19 outbreak. Following the launch of the PPP program – offering forgivable loans to small firms for payroll, expenses, and other qualifying expenditures – loan applications spiked significantly and millions of firms are expected to benefit from the nearly $800 billion worth of forgiven loans that the SBA issued up until 2022.
- Statistics on small company loans reveal that demographic groups vary greatly in their access to credit. Businesses run by women and minorities often face difficulties accessing financing; according to SBA records, only 16% of 7(a) loans granted were for women-owned firms in fiscal year 2022 versus 27% being granted for minority-owned businesses.
- Non-bank financing solutions, including Internet lenders and alternative lending platforms, have grown increasingly popular over time. These platforms provide small businesses with faster and simpler funding solutions should they not meet bank loan criteria. Now small company owners who need capital have additional sources available thanks to non-bank funding options.

(Source: hostinger.in)
Small Business Loans by Region
Regional variations in small company loan data can be explained by factors like the economic climate, industry composition, and lending standards.
- Northeast states such as Pennsylvania, Massachusetts, and New York boast a healthy environment for small company financing. Numerous strong companies are located here including banking, technology, and healthcare firms that help make financing options more readily accessible. Furthermore, New York City provides access to conventional funding sources via large banks and financial institutions that facilitate conventional funding streams.
- Southeast states such as Florida, Georgia, and North Carolina boast a vibrant small business scene that encompasses numerous states like Florida. Non-bank financing alternatives like Internet lenders and alternative finance platforms have become more prominent across this region, giving small enterprises greater access to funds especially in underdeveloped areas. Furthermore, small community banks exist throughout this region that serve local businesses.
- Midwest states include Illinois, Ohio, and Michigan with both urban and rural regions present. Manufacturing and agriculture play an influential role in small company loans in this region; larger banks and online lenders tend to dominate metropolitan centers while community banks and credit unions play an integral part in providing small company funding in smaller towns or rural regions.
- States like California, Washington, and Colorado comprise the West region, known for its bustling business scene and innovation hubs. Sectors including technology, entertainment, and hospitality all affect small company financing in this region; venture capital networks as well as angel investor networks are very prominent throughout. Angel investment networks help finance start-ups as well as fast-growing companies in this part of the United States.
- Southwest area states such as Texas, Arizona, and New Mexico offer a diverse environment for small businesses. This region is well known for its dynamic business culture that spans construction; healthcare and energy. Furthermore, conventional banks, local lenders, and internet platforms all promote lending for these enterprises.
Small Business Loan by Demographic
Statistics on small company loans by the demographic group provide insight into differences in accessing financing across different entrepreneur groups. Based on available data, below are some insights regarding the demographics of small company loans.
- Women business owners may find it harder than male owners to secure small company loans. According to the Federal Reserve Small Business Credit Survey for 2022, women-owned firms had a higher percentage of loan denials (27% vs 19%) and more often received smaller loans overall.
- Minority-owned small company loans can be difficult to come by for minority entrepreneurs – particularly Black, Hispanic, Asian, and other minority owners. According to a Federal Reserve report on loan refusal rates by race or ethnic groupings, Black-owned businesses had the highest loan refusal rate (34%). Hispanic-owned businesses experienced significantly higher denial rates (25% vs 15% for white-owned).
- Veterans running small enterprises often benefit from access to special lending programs and support from the Small Business Administration (SBA), including Patriot Express Loan Program and Veterans Advantage Program loan options. These initiatives seek to make it easier for veterans to start or expand their small enterprises by giving them access to funding.
- Small firms in rural areas are more likely to be approved for loans, with 51% receiving all of the funding they requested.
- Rural small companies depend heavily on smaller banks for loan applications; 62% of loan applications to such institutions come from rural companies themselves.
- Young entrepreneurs in the millennial and Gen Z age groups may face difficulty accessing small company funding due to inexperience or poor credit histories; unfortunately, however, little information exists that provides specific statistics regarding loans provided solely to young business owners.
- Small enterprises in disadvantaged locations or populations with lower incomes often find it hard to gain access to funding. It could be that these areas lack traditional lending institutions or face economic issues that prevent lenders from providing funds; government programs and initiatives such as community development financial institutions (CDFIs) aim to reduce these inequities by giving money directly to firms operating in these deprived regions.
- Due to market restrictions and distance from financial institutions, small firms located in rural locations often experience difficulty securing business loans. Luckily, initiatives and programs like Rural Business Development Grants from the Small Business Administration (SBA) and USDA’s Rural Microentrepreneur Assistance Program help foster small business development in these locations.

(Source: Guidantfinancial.com)
Small Business Loans by Lenders
Statistics on small company loans may shed some light on how different lenders approach lending practices differently.
- Small company financing has historically been provided by traditional institutions like large national and local banks. According to the Federal Reserve’s Small Company Credit Survey for 2022, major banks granted about 38% of loan applications while 61% went through small banks. Furthermore, these banks may also offer other forms of lending products including term loans, lines of credit, and SBA loans for their small company clients.
- Online lenders have become an increasingly popular source of funding for small businesses, offering them new sources of funds through loan application and approval processes that use technology. According to estimates by the Federal Reserve, 24% of small company loan applications granted will come through online lenders by 2022; they offer services to customers with poor or limited credit histories alike.
- Credit unions can be an invaluable source of funding for local small enterprises, providing personalized service at competitive pricing. According to estimates by the National Association of Federally-Insured Credit Unions (NAFCU), credit unions would have granted loans totaling $75 billion by 2022.
- CDFIs (Community Development Finance Institutions), specialist lenders, are dedicated to financing underprivileged areas and companies that may find it hard to obtain traditional funding sources. Their mission is essential in spurring economic growth while eliminating loan inequities; according to estimates by The Opportunity Finance Network, CDFIs provided small companies loans totaling $6 billion by 2022!
- As part of its efforts to support small firms, the Small Business Administration offers various lending programs, such as its 7(a) loan program and 504 loan programs. Both provide assurances to lenders so that they will lend money to startup companies who might otherwise not qualify – the SBA issued over $22 billion worth of 7(a) loans in FY 2022 alone!
- Peer-to-peer lending services and crowdfunding websites have become more widely utilized as alternative financing channels for small businesses. These online marketplaces connect lenders to either individual or institutional investors. Although alternative lending platforms still account for only a minority market share compared to traditional lenders, their popularity continues to increase rapidly.
Small Business Loan by Industry
Due to different industries’ company requirements, risk appetites, and financing needs, small company loan data may vary drastically by industry. Below are some insights into small company lending statistics by industry.
- Construction firms often need large sums of money for labor, supplies, and equipment expenses. According to the Federal Reserve’s Small Business Credit Survey, more construction companies sought borrowing than other industries in 2022 – about 50% requested finance and 47% were approved for their full request amount.
- Small boutiques and giant department stores are both part of the retail sector, but loans may also be necessary for equipment, expansion, or inventory purchases. According to data released by the Federal Reserve in 2022, approximately 43% of small retailers applied for financing loans, and 55% received their full amounts requested.
- Loans available from the Small Business Administration (SBA) do not apply to at least eleven potential industries that could legitimately benefit.
- Loans can be useful to manufacturing companies for working capital needs, facility expansion, and equipment improvements. According to the Small Business Credit Survey, 42% of small manufacturers sought funding in 2022 with 56% receiving approval according to applications submitted for funding.
- Professional service businesses like consulting companies, law offices, and accounting firms often rely on loans for operating cash flow or technological expenditures. According to the Federal Reserve data from 2022, 36% of small professional service businesses requested financing and 58% were approved with all of their requests being approved completely.
- Loans are frequently sought by businesses in the healthcare sector – hospitals, clinics, and pharmacies – for working capital requirements, equipment acquisition, and facility expansion purposes. According to the Small Business Credit Survey in 2022, 48% of healthcare businesses that requested finance were approved.
- Hotels; restaurants; and cafes are companies in the lodging and food services sector; that often need loans for remodeling projects; equipment improvements; or operating capital needs. According to estimates from the Federal Reserve Bank of St Louis in 2022; around 33% of small enterprises within this industry submitted loan applications with 47% acceptance rates.

Small Business Loan Application Statistics
Statistics on small company loan applications offer insight into their patterns, difficulties, and outcomes.
- Application rates for small business loans will depend on the market, firm type, and funding availability; according to the Federal Reserve’s Small Business Credit Survey from 2022, around 40% of small firms apply for credit.
- Small companies often find it challenging to secure loans. Creditworthiness, financial stability, and lending requirements all play a part in loan denial rates – according to the Federal Reserve’s Small Company Credit Survey approximately 20% of applicants will not receive funding in 2022.
- Small businesses seeking loans from conventional banks, credit unions, internet lenders, and alternative finance platforms may apply with various lenders for financing; the application procedure and approval rates depend on which lender is chosen; according to estimates by the Federal Reserve in 2022, small banks approved about 61% of applications compared with large banks that approved 38%.
- Now, 32% of loan requests from small firms come from non-bank lenders.
- Credit problems cause 20% of small company loans to be rejected.
- Small firms requesting loans from the Small Business Administration may need loans of various amounts depending on their financial requirements and sector. According to SBA reports, in fiscal year 2022 the average loan amount under its 7(a) program averaged $536,000 but depending on size, type, and purpose could differ significantly.
- Small companies seek loans for various purposes, including working capital needs (46%) followed by equipment purchases (41%), growth opportunities (41%), funding inventory needs, or debt refinancing (36%). According to a poll conducted by the Federal Reserve Banks.
- Small company loan applications can take time and work. Owners of small businesses must gather together all the required paperwork, complete forms, and navigate underwriting procedures before being granted loans – according to one Biz2Credit survey, owners averaged 33 hours applying for loans each time!
- COVID-19 had a profound effect on loan applications from small businesses. According to estimates from the Small Business Administration; loan applications rose between 2020-2022 thanks to initiatives; like Paycheck Protection Program loans. Over $800 billion; worth has already been approved; through this program – providing millions of enterprises with vital assistance.

(Reference: zippia.com)
Impact of Small Business Loans on the Economy
Small company loans play a pivotal role in driving economic development by stimulating innovation, job creation, and expansion of economic activity. Here are some impressive statistics that showcase this impactful financing source.
- Small firms are an essential force behind job creation in this country. According to estimates by the U.S. Small Business Administration (SBA), they were responsible for 64% of new employment between 2020-2022 – through expanding operations, hiring additional staff, or taking advantage of financial solutions designed specifically for small firms.
- Small enterprises play an integral part in our economy. According to estimates by the Small Business Administration (SBA), small enterprises will account for 44% of economic activity in 2022 in the United States. With access to funding provided through loans for small businesses, these enterprises may increase productivity and economic output by investing in tools; technology, and other resources through loans for small businesses.
- Small company loans are integral in increasing Gross Domestic Product (GDP). According to research by Federal Reserve Banks; research shows that GDP increases of small firms with credit needs can increase significantly; by as much as $2.50 to $3.00 for every $1 increase in small company credit needs.
- Small company loans foster innovation and entrepreneurship by giving prospective businesspeople access to capital needed to fund innovative new projects, market pioneering goods or services and stimulate economic development. According to the Small Business Administration (SBA), small enterprises represented 46% of private sector production while 50% employed people within that sector.
- Small company loans are essential to regional and local economic development and regeneration. By helping firms start up or expand in underdeveloped regions, small company loans help close financial gaps among these local small firms, increasing economic activity while simultaneously improving quality of life.
- Small company loans have far-reaching ramifications on the economy via vendor and supply chain networks. Small firms receiving financing might increase the number of other small firms they buy from, leading to greater demand and subsequently raising ecosystem income levels overall.
- Accessing small company financing strengthens economic resilience. Small firms may encounter difficulties with cash flow during economic downturns or crises, leading to reduced sales. Small company loans provide crucial assistance that allows these firms to survive tough times while keeping jobs and contributing to economic stability.

(Reference: guidantfinancial.com)
Small Business Loan Trends and Predictions
Trends and forecasts related to small business loans provide stakeholders with insight into the ebb-and-flow of financing markets for companies of all types, helping them anticipate changes that may occur over time.
- Recent years have witnessed a remarkable surge in online lending platforms. Online lenders provide small firms who may otherwise find difficulty borrowing money from traditional banks with ease, faster approval times, and funding availability – driving an upward trend for the growth of these platforms due to digitalization and technology use.
- Small enterprises are increasingly turning away from traditional bank funding solutions and turning toward non-bank options like peer-to-peer lending, revenue-based financing, merchant cash advances, and crowdfunding as alternatives to bank funding sources. These alternatives provide flexible terms, quicker funding speeds, and creative repayment plans – perfect solutions for small firms requiring tailored finance sources that meet specific demands.
- Government loan programs for small businesses, including those offered by the Small Business Administration (SBA), are expected to play an increasingly significant role in lending. Such initiatives provide banks with assurances and rewards when lending money to startups that don’t fit traditional lending criteria, like those found through 504 and 7(a) loan programs provided by SBA. Its loan programs should further encourage company development and entrepreneurship.
- To facilitate underrepresented groups such as firms run by women, minorities, and enterprises in underprivileged areas, inclusive lending policies have come to be increasingly prioritized. Equal access to finance is crucial and lenders and governments alike have begun taking measures to minimize loan discrepancies more actively; initiatives to advance inclusion and diversity through lending will likely continue in coming years.
- Lenders are increasingly turning to technology and data analytics in order to make more effective loan decisions. Lenders can more quickly assess creditworthiness for companies without credit histories when given access to alternative data sources such as transaction history, social media analytics, or cash flow information. Underwriting procedures will increasingly include machine learning/artificial intelligence algorithms allowing for quicker loan reviews with greater precision.
- Risk and loan portfolio management have become top priorities for lenders in light of economic uncertainties brought on by events like the COVID-19 pandemic. Lenders will make sure their lending practices remain strong and stable by improving underwriting standards, conducting stress tests on portfolios, and creating risk management frameworks.
- ESG factors are becoming more influential when lending to small businesses, as lenders and investors increasingly consider how an enterprise will affect the environment and community when making their lending decision. Small enterprises may find success securing financing if they demonstrate sustainable practices, social responsibility, and excellent governance practices.

(Reference: Guidantfinancial.com)
Bottom Line
Small company loans are essential in supporting entrepreneurs and their companies as they expand and succeed. Small company loan data provide lenders, policymakers, and small company owners a valuable insight into trends, issues, and opportunities within the financing marketplace. These figures highlight the loan amounts, approval rates, and uses for which small firms seek financial support.
Furthermore, they demonstrate how loans to small companies contribute to regional and national economies by creating jobs, expanding economic activity, and sparking innovation. Furthermore, this data underscores the need to address demographic disparities in lending access – especially among minority- and women-owned enterprises – through inclusive lending methods or financial products designed specifically to bridge those gaps for equal chances for all.
COVID-19 has increased awareness of small company loans as government initiatives such as PPP were critical in providing emergency capital to struggling companies during difficult times. Stakeholders can create targeted plans, implement policies, and make educated decisions by staying current with information regarding small company loans – this will enable their own small companies to flourish more successfully while simultaneously supporting employment, creating economic vitality in local communities, and contributing to overall economic health. Small company loans provide a lifeline to business owners while simultaneously expanding operations, creating employment, and boosting the general prosperity of local communities and the economy overall.
What percentage of small firms are in debt?
74% of small and midsized US firms – according to a Statista poll from 2022 – reported having debt, as reported by the Federal Reserve’s most recent statistics in 2017. On average, small company loans amount to an average of $663K loan amount between 2017-2018. Debt may be necessary in order for firms to achieve success;
Why are small firms finding it so hard to secure financing?
If a project or company is considered too risky for banks to back, or they impose an exorbitantly higher interest rate that small enterprises simply cannot pay, these small enterprises don’t have access to the financial markets due to being too small while their owners don’t possess enough assets on hand for additional funding if needed.
What causes cash flow issues for small businesses
Many businesses struggle with their cash flow due to failing to meet their profit goals while being unaware that this is occurring. For example; if your client pays you in 30 days but your payroll payment is due today without sufficient earnings available (this would constitute your working capital requirement), problems ensue.
What Is an Appropriate Lending Rate?
5.99% to 9% are considered appropriate personal loan interest rates; according to the Federal Reserve’s estimates for annual percentage rates for two-year bank personal loans with APRs as low as 5.99% and below for creditworthy customers.

Barry Elad
Barry is a lover of everything technology. Figuring out how the software works and creating content to shed more light on the value it offers users is his favorite pastime. When not evaluating apps or programs, he’s busy trying out new healthy recipes, doing yoga, meditating, or taking nature walks with his little one.
More Posts By Barry Elad
[ad_2]
Source link
